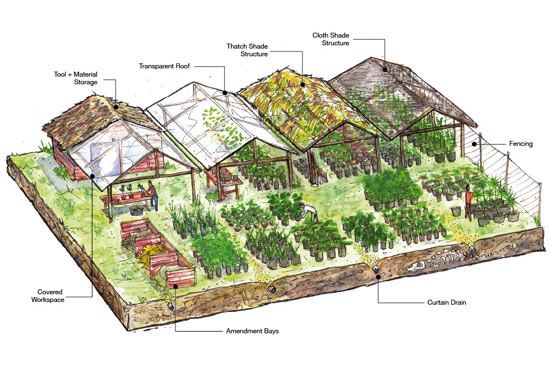
Wet-dry Nursery Development And Operation
Integrated Pest Management (IPM) is an approach to managing insects, mites, pathogens, nematodes, weeds, and other pests in which multiple practices are implemented throughout the entire production period of the crop. IPM can be viewed as a series of steps that is repeated or modified as needed: Prevention/avoidance, Monitoring, Decision making, Intervention, Evaluation.
IPM includes judicious use of pesticides in careful coordination with other pest management practices. Restricted labeling of pesticides, pest resistance, safety to nursery personnel, and environmental issues are all concerns to Plantations International.
In addition, nursery crop production requires highly technical and specialized production skills, particularly with respect to propagation. In addition to a fundamental and practical understanding of plants and how they grow, nursery operators require an understanding of the specific growing requirements of each crop and how these growing conditions can be managed to achieve efficient production. The importance of the best quality planting material as an initial investment is a well realized factor for persons engaged in Horticulture field. So nurseries have great demand for the production of plants, bulbs, rhizomes, suckers & grafts. But in general good quality & assured planting material at reasonable price is not available and we at Plantations International invest in growing our future plants under controlled conditions.
Site location – Factors to be considered when evaluating tree nursery sites include:
- soil type and conditions
- environmental conditions including rainfall, wind and slope of the land
- access to water for irrigation
- proximity to markets
- access to good roads
- access to labor
- room for future expansion
- zoning requirements or limitations
- potential environmental hazards such as industrial pollution or contaminated water
Equipment requirements
- The basic requirements for a nursery operation include:
- Irrigation equipment
- Field equipment such as tractors, trailers and cropping equipment
- Sprayers for control of weeds, insects and diseases
- Sterile rooms
- Multiplication processes
- Office equipment
- Plantations International explains that nurseries are classified into the following types:
- Seedling nursery: A nursery which has only seedling beds, i.e., in which seedlings only are raised, no transplanting being done is called seedling nursery.
- Transplant nursery: A nursery which has only transplant beds, in which seedlings are transplanted for preparation for forest planting is called transplant nursery.
- Dual nursery: A nursery that combines both a seedling and transplant nursery.
- Plantations International’s Permanent Nurseries are nursery’s that are maintained for supplying nursery plants for a long time on a permanent basis. It is intended to meet the requirements of one or more ranges and it is relatively larger in extent.
Main features
- Fit for large and intensive work and intensively managed
- Established where all the facilities are available, i.e., easy supervision, communication facilities, labors, etc.
- Intensive Manuring and soil working are done in perpetuity.
- Used for large scale forestry and farming projects, and/ or distribution to the villagers under community and private forestry program.
- A large labor forces, tools and equipment are available.
- Original cost of formation is high but is cheaper in the long run.
- Skilled supervision 7 days a week.
Advantages
- Varieties of planting stocks supply; such as root- shoot cuttings, grafted plants, layering, budding, poly-pot seedlings, etc.
- Each nursery crop requires specific growing practices to improve the quality of the plant. These practices include pruning, as well as control of weeds, insects and diseases.
- Duration of service life is long and production cost is reasonable.
- Meet the requirement of more ranges.
- Supervision cost is low and can be easily supervised.
- Easy transport of nursery stocks due to nearness of roads.
- Plants are raised year after year for a long time on same site.
Key production requirements in producing nursery crops from seed include the following:
- A good source of seed from a hardy location
- Proper storage conditions for each crop species to maintain seed viability (key requirements are moisture content, storage temperature and relative humidity)
- seed treatments to break the dormancy of the seeds germination requirements.
Plantations International best management practices empower our container and field-grown plant production to operate at a higher level of efficiency and effectiveness while implementing proactive management practices necessary to produce plants with minimal environmental impact.